What is the Inbound Routes Module used for?
When a call comes into your system from the outside, it will usually arrive along with information about the telephone number that was dialled (also known as the "DID") and with the Caller ID of the person who called.
The Inbound Routes Module is used to tell your FreePBX/Asterisk system what to do with calls that come into your system on any trunk that has the "context=from-trunk" parameter in the PEER details.
The Inbound Routes module works together with most of the other Modules in FreePBX. Calls come into your system on Trunks that are configured in the Trunks Module. The Inbound Routes Module then tells FreePBX/Asterisk where to send these calls. Calls can be sent to a variety of destinations, including an Extension, a Ring Group, a Queue, an IVR, a Time Condition, a Feature Code, a DISA, a Conference, etc., all of which are configured in their own Modules.
Overview
Inbound routing is one of the key pieces to a functional PBX. The Inbound Routes module is themechanism used to tell your PBX where to route inbound calls based on the phone number or DID dialled. This module is used to handle SIP, PRI and analog inbound routing. Setting up inbound routing properly is a critical step in the deployment of a PB system. Inbound routes are often used in conjunction with time conditions and IVR’s. A typical setup will go from an inbound route to a time condition, then to an IVR or after hours answering service depending on the time condition met.
Adding an Inbound Route
The PBX allows two specific types of inbound routing: DID & CID Routing. These two routing methods can be used on their own or in conjunction with one another. Leaving both fields blank will create a route that matches all calls. The “Add Incoming Route” has four options as shown in this screen shot.
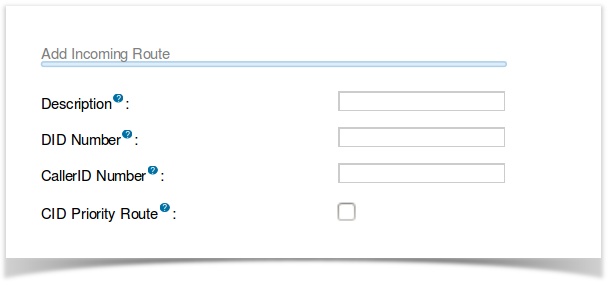
Description
Enter a unique description for the route.
DID (Direct Inward Dialling)
Routing calls based on the trunk on which the call is coming in. In the DID field, you will define the expected “DID Number“ if your trunk passes DID on incoming calls. Leave this blank to match calls with any or no DID info. The DID number entered must match the format of the provider sending the DID. You can also use a pattern match to match a range of numbers. Patterns must begin with an underscore (_) to signify they are patterns. Within patterns, X will match the numbers 0-9 and specific numbers can be matched if they are placed between square parentheses. This field can also be left blank to match calls from all DIDs. This will also match calls that have no DID information.
CID (Caller ID)
Routing calls based on the caller ID number of the person that is calling. Define the caller ID number to be matched on incoming calls. Leave this field blank to match any or no CID info. In addition to standard dial sequences, you can also put “Private,” “Blocked,” “Unknown,” “Restricted,” “Anonymous” or “Unavailable” in order to catch these special cases if the telco transmits them.
CID Priority Route
The default priority levels are matched in the following sequence:
- Routes with a specific DID and CID will always be first in priority.
- Routes with a specific DID but no CID will be second in priority.
- Routes with no DID, but with a specific CID will be third in priority.
- Routes with no specific DID or CID will be last in priority.
Toggling this field will make the CID a priority only if there is no entry in the DID field.
Options
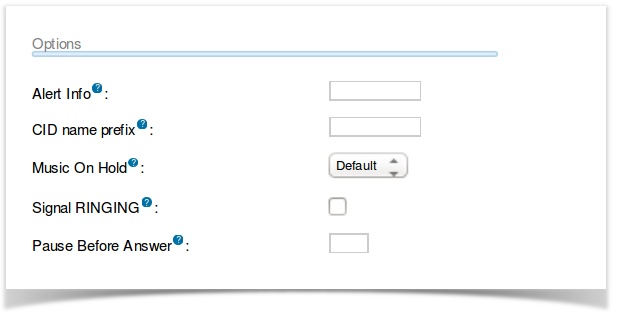
Alert Info
This is used to send a string of text in the SIP ALERT_INFO headers. It’s often used for SIP endpoints that ring differently or auto-answer calls based on the ALERT_INFO text that is received.
CID name prefix
This allows text to be prepended to the caller ID name information from the call. This is often used to identify where a call came from. Calls to a number dedicated for sales might be prefixed with ”Sales:.” A call from John Doe would display as, “Sales:John Doe.”
Music On Hold
MoH allows you to define the specific music on hold for calls on this inbound route. Whenever a caller is placed on hold, they will hear the music on hold defined here. This is typically used for companies that advertise in their music on hold and take calls in multiple languages. Calls to an English DID might play English advertisements and calls to a Spanish DID would play Spanish advertisements.
Signal RINGING
This toggle will send “ringing” tones before the system lets the other side know that the call has been answered. Some providers and devices require this. You’ll notice the need for this if you can send calls directly to a phone/extension, but if you send it to an IVR, it won’t connect the call.
Pause Before Answer
An optional delay to have the PBX pause before processing this route. This is not really useful on digital connections, but may be handy if external fax, modem or security systems are installed on the trunk and you would like them to be able to seize the line prior to the PBX answering the call.
Other Settings
Other settings depend on installed modules. You may have more setting than are shown here, or settings may be missing.
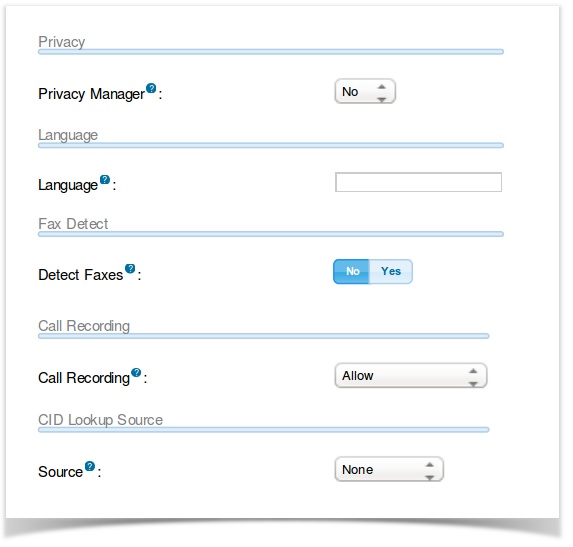
Privacy Manager
Enable or disable the PBX “Privacy Manager” functionality on this route. When enabled, calls without an associated caller ID will be prompted to enter their 10-digit telephone number. Callers will have 3 attempts to enter this information before the call is disconnected. If a user/extension has call screening enabled, the incoming caller will be prompted to say their name when the call reaches the user/extension
FAX DETECT SECTION
For Quality Control, Voxis does not permit T.38 over our voice network, faxing will not work, please select No. Voxis has a separate fax network and faxing services for your faxing needs
CID LOOKUP SOURCE SECTION
Source
A CID lookup source lets you specify a source for resolving numeric caller IDs of incoming calls. This gives you more detailed caller ID information and CDR reports. The sources are defined in the Caller ID Lookup Sources module and can be linked to web based services, local databases or CRM systems. Lookup sources are also useful if your trunks do not pass the caller ID name information with the number.
LANGUAGE SECTION
Language
This allows the language setting to be configured before hitting a destination. This is useful, when you use privacy manager and want to have the prompts played in the proper language. Please note that not all of the voice prompts are recorded in every language. If the prompt is not available, it will play in the default English setting. If this is left blank, the system will default to English.
The available language codes are:
- English - en
- Chinese - cn
- German - de
- Spanish - es
- French - fr
- Hebrew - he
- Hungarian - hu
- Italian - it
- Portuguese - pt
- Portuguese (Brazil) - bp
- Russian - ru
- Swedish - sv
Call Recording
This setting controls or overrides the call recording behavior for calls using this route.
Allow
This will honor the normal downstream call recording settings.
Record on Answer
Starts recording when the call would otherwise be recorded, ignoring any settings that say otherwise.
Will start recording right away, capturing ringing, announcements, MoH, etc.
Never
This will disallow recording regardless of downstream settings.
SET DESTINATION SECTION
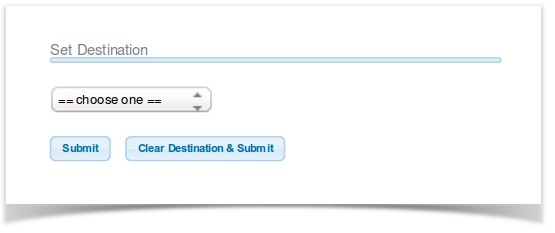
The PBX provides multiple ways to route a call. This is the place where the desired call target is selected.